flowchart LR
A[Organism] --> B[Molecular Analysis]
B --> C{DNA Methylation}
C --> D[WGBS]
C --> E[MBDBS]
C --> F[RRBS]
C --> G[qPCR]
[ ]
]
Take Home Points
Trigg et al. (2022)
[ ]
]
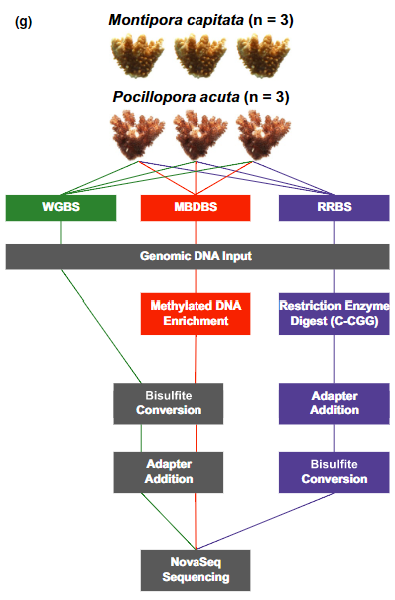
We evaluated the performance of three approaches that use bisulfite-treated DNA for library preparation to enable single base-pair resolution quantification of DNA methylation in corals.
whole genome bisulfite sequencing (WGBS)
methyl-CpG binding domain bisulfite sequencing (MBDBS)
reduced representation bisulfite sequencing (RRBS)
Taken together, our findings indicate biology, genome architecture, regions of interest, and depth of coverage are critical considerations when choosing methods for high-resolution quantification of DNA methylation profiles in invertebrates.
Our results demonstrate that the methylation landscape can vary significantly across species, which is a critical consideration for both interpreting environmental response capacity, and for experimental design.
Together these metrics enable comparative capacity for three common methods in two coral taxa that vary in their phylogeny, genome size, symbiotic unions and environmental performance, and provide the community with a more comprehensive foundation upon which to build laboratory and statistical analyses of DNA methylation, plasticity and acclimatization.
Tang et al. (2023)
[ ]
]
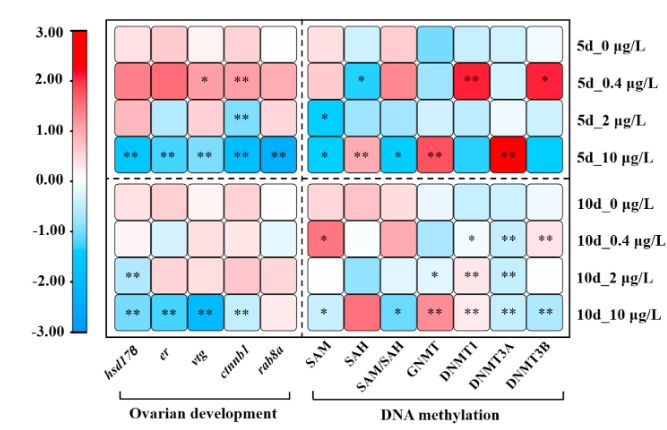
We aimed to explore the purpose of exploring the mechanism of reproductive endocrine disruption and DNA methylation in female C. farreri under stress from B[a]P by detecting the gonad index, hormone content, ovarian development, and indicators related to DNA methylation in the ovary.
- We speculate that B[a]P stress may affect DNA methylation of key genes involved in steroid hormone synthesis.
- It has been reported that abnormal gene expression and related toxicological effects after exposure to pollutants may be caused by DNA methylation.
The high methylation level of hsd17β promoter may be one of the reasons for the reproductive toxicity of C. farreri caused by B[a]P stress.
- Recent studies have found that abnormal methylation of promoters in key reproductive genes has endocrine disrupting effects on mammals and teleost fish after exposure to POPs.
Team used qPCR and specific primers to find that the results of the analysis showed that the methylation level of the er promoter was low and that B[a]P had no obvious effect on the level of DNA methylation of female scallops at different concentrations and times.
Scientific Relevance / Impact
As both papers discuss, the experimental design as well as the biology of the organism are crucial to understand as clearly as possible. What are your goals, one target gene or many? Transcription alteration or gene silencing? Do you have a reference or not?
All of these question lead to the big dog, how much money is there and what do you need to prove your hypothesis? For a single function/ gene/ enzyme, the cost of primers and qPCR supplies may be all that we need. Do you need to characterize a whole chunk of genome? Maybe RRBS before looking to WGBS.
Having multiple methods supports diversity in questions asked and answered with the flexibility to obtain only the data you need versus being inundated with an expensive and data-dense output that takes too many man-hours to process.
Reflection/ Through-line
Thinking of the connection from understanding how to use molecular analysis, top techniques to understanding molecular manipulation, and finally ending up in a methods blitz that is evolving in realtime to provide best, practical, and reproducible ways to get at the answer.