What's a Weka going to do?
Here I want to examine how Machine Learning might compare with a our conventional gene expression analysis. The data set includes both male and female oysters exposed to OA conditions (and controls). Gonad tissue. Sam ran data through bowtie/stringtie for comparison. Complete sample details are below. PDF of post
| Sample.ID | OldSample.ID | Treatment | Sex | TreatmentN | Parent.ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12M | S12M | Exposed | M | 3 | EM05 |
| 13M | S13M | Control | M | 1 | CM04 |
| 16F | S16F | Control | F | 2 | CF05 |
| 19F | S19F | Control | F | 2 | CF08 |
| 22F | S22F | Exposed | F | 4 | EF02 |
| 23M | S23M | Exposed | M | 3 | EM04 |
| 29F | S29F | Exposed | F | 4 | EF07 |
| 31M | S31M | Exposed | M | 3 | EM06 |
| 35F | S35F | Exposed | F | 4 | EF08 |
| 36F | S36F | Exposed | F | 4 | EF05 |
| 39F | S39F | Control | F | 2 | CF06 |
| 3F | S3F | Exposed | F | 4 | EF06 |
| 41F | S41F | Exposed | F | 4 | EF03 |
| 44F | S44F | Control | F | 2 | CF03 |
| 48M | S48M | Exposed | M | 3 | EM03 |
| 50F | S50F | Exposed | F | 4 | EF01 |
| 52F | S52F | Control | F | 2 | CF07 |
| 53F | S53F | Control | F | 2 | CF02 |
| 54F | S54F | Control | F | 2 | CF01 |
| 59M | S59M | Exposed | M | 3 | EM01 |
| 64M | S64M | Control | M | 1 | CM05 |
| 6M | S6M | Control | M | 1 | CM02 |
| 76F | S76F | Control | F | 2 | CF04 |
| 77F | S77F | Exposed | F | 4 | EF04 |
| 7M | S7M | Control | M | 1 | CM01 |
| 9M | S9M | Exposed | M | 3 | EM02 |
Sam provided me with a table of FPKM values pulled from Ballgown. There is information for about 39k genes. In short I believe Sam got no DEGs with record to treatment, but as might be expect many differences based on sex.
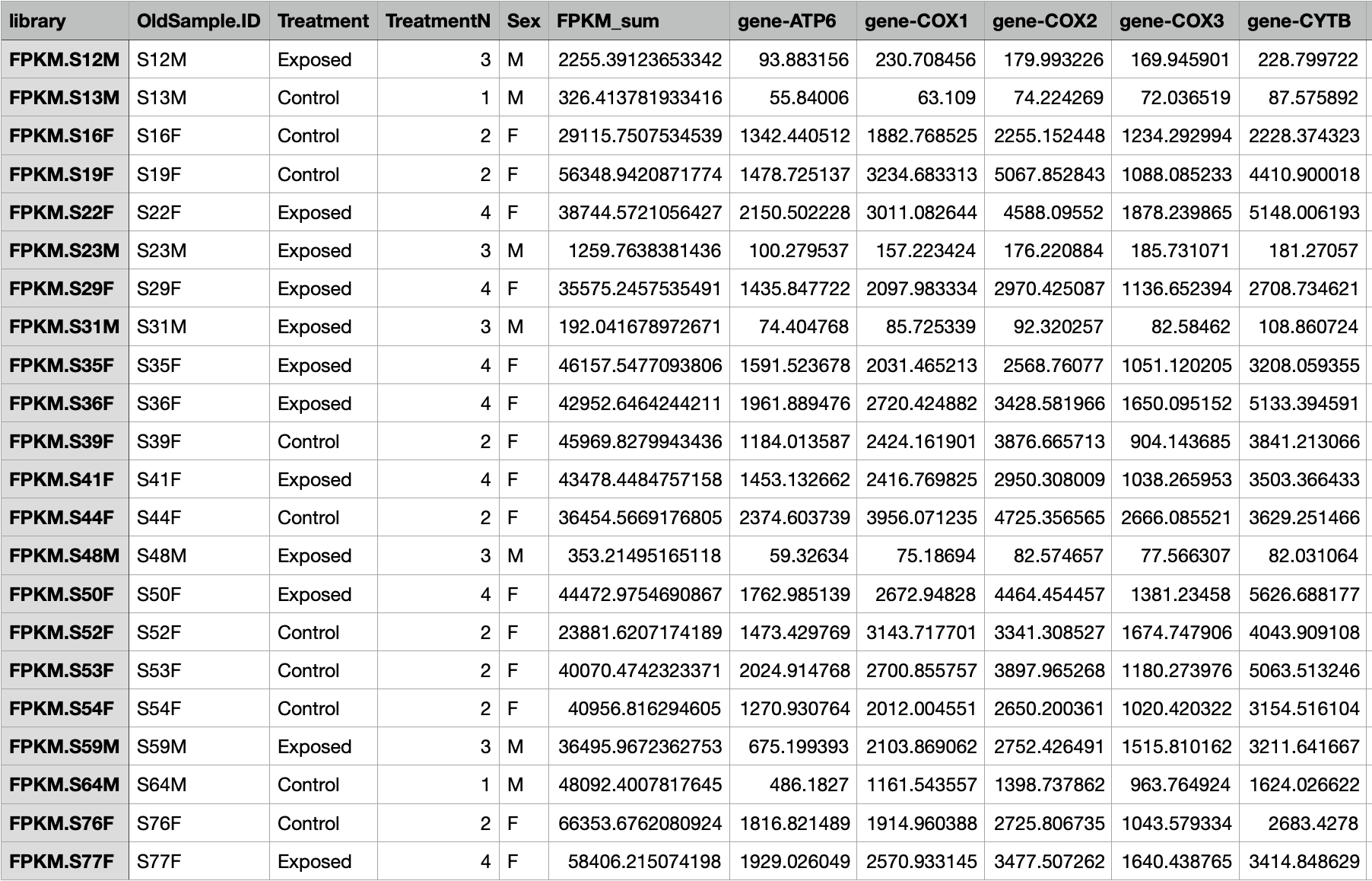
I opened the csv file up in the Weka Explorer.
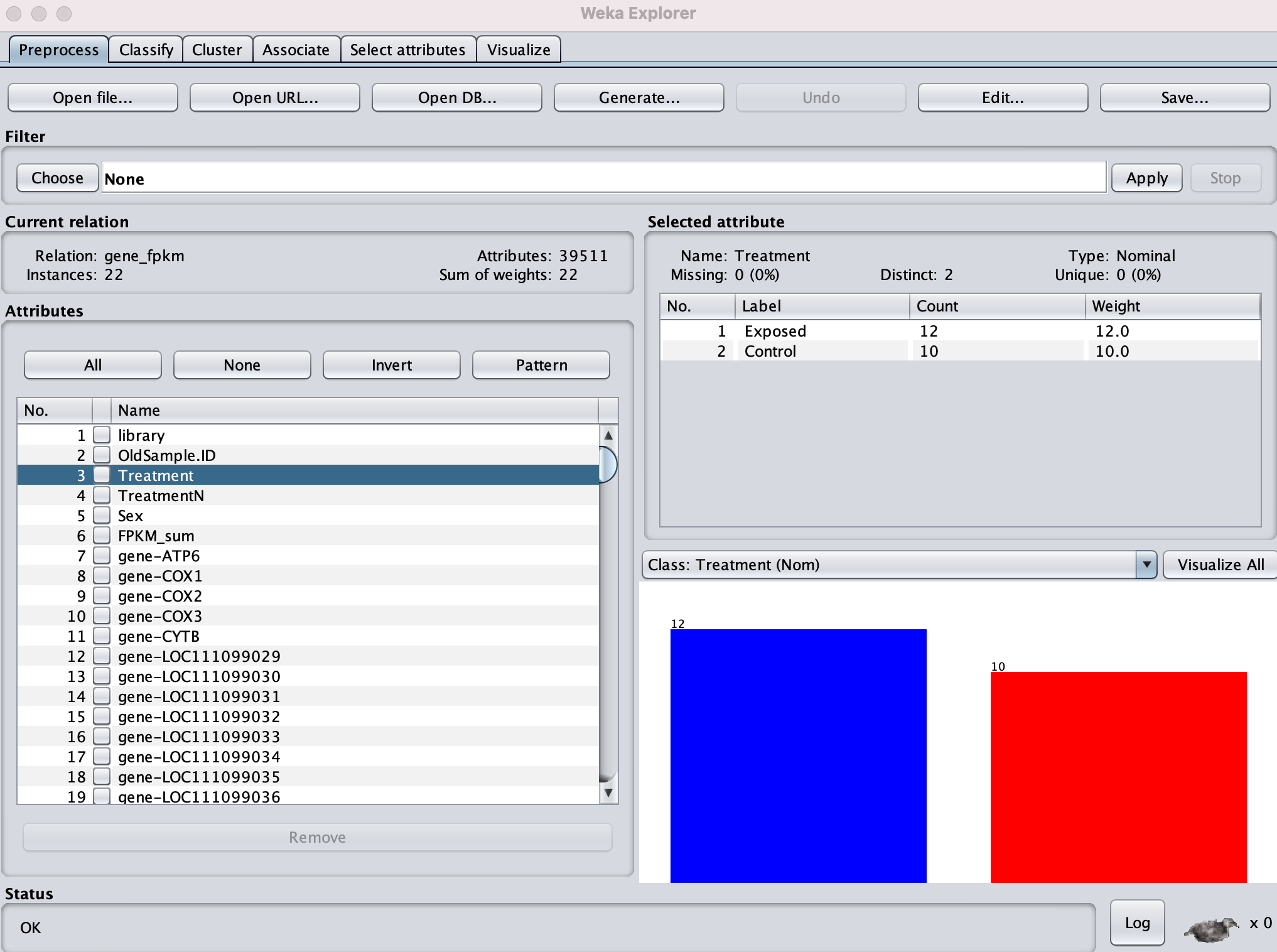
Then ran Classifier using SMO, on Treatment (thus ignoring sex). Correctly Classified Instances = 59.09%
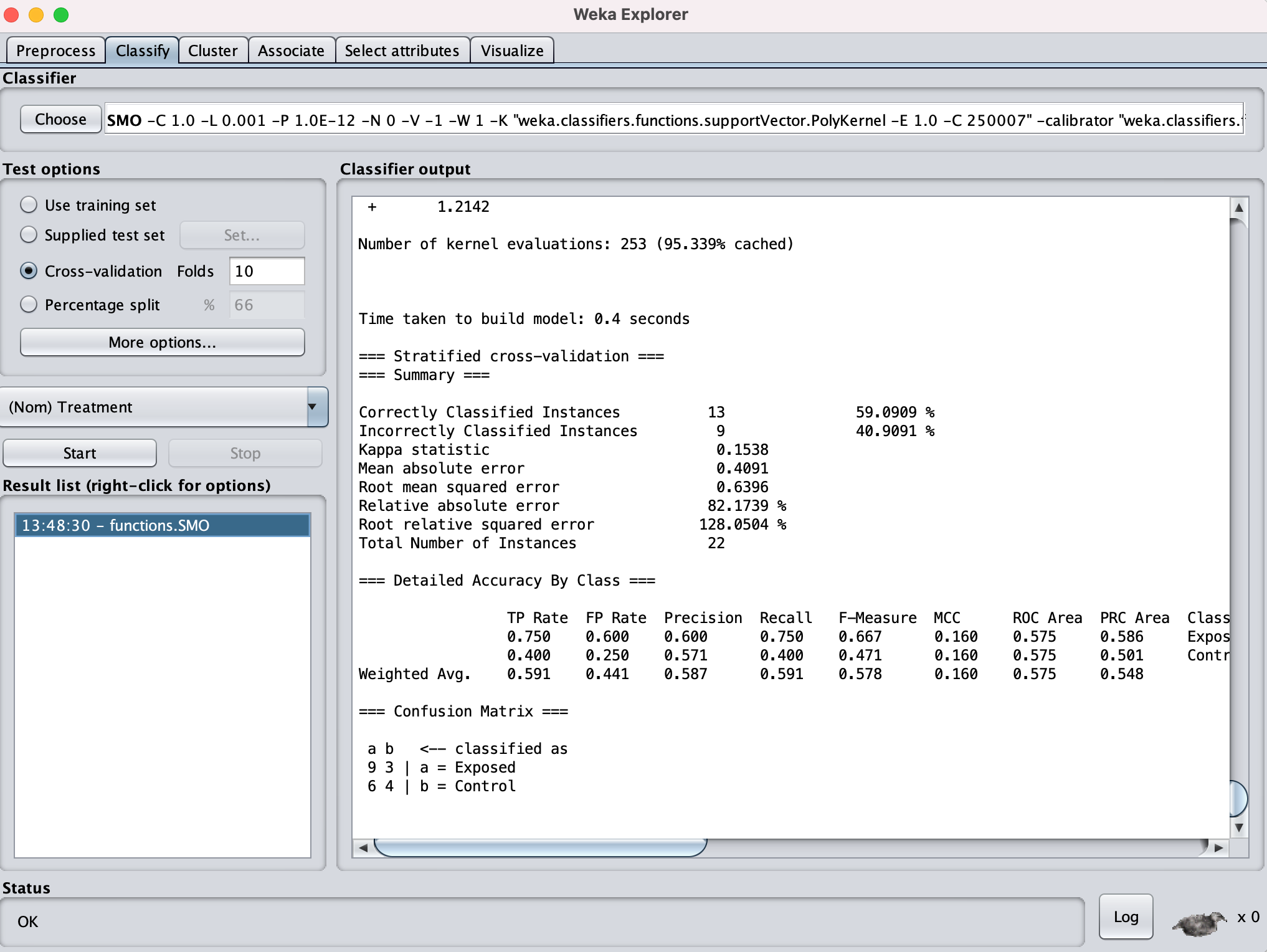
I went on to Select Attributes
Based on this I found 24 genes contributing ranging in Ranked attributes values from 0.5 to 0.7743.
My goal now is to rerun this pipeline in Weka just using data from these 24 genes to see if the predictability improves. Will be doing some inelegant data munging with bbedit, excel, and Rstudio.
Step 1) simply read in Sam’s fpkm table with 39k genes.
fpkm <- read.csv(file = "../analyses/gene_fpkm.csv")
Step 2) generate list of genes I can insert into a dplyr::select function. (skip this part if adverse to cringing)
Paste into excel, copy gene column, paste back into bbedit:
Text::remove line breaks
Find::replace gene- with gene. (due to Weka formatting?)
Find::replace ` ` with ,
Paste in dplyr::select code chunk
select05.treat <- select(fpkm, Treatment, TreatmentN, Sex, gene.LOC111128233, gene.LOC111105393, gene.LOC111116464, gene.LOC111135088, gene.LOC111130500, gene.LOC111127278, gene.LOC111113969, gene.LOC111132481, gene.LOC111105938, gene.LOC111138283, gene.LOC111131835, gene.LOC111129832, gene.LOC111130487, gene.LOC111127862, gene.LOC111110254, gene.LOC111124688, gene.LOC111125297, gene.LOC111116779, gene.LOC111119607, gene.LOC111123744, gene.LOC111124204, gene.LOC111113829, gene.LOC111110051, gene.LOC111104660)
Then writing it out as
write.table(select05.treat, file = "../analyses/select05.treat.csv", sep = ",", row.names = FALSE, quote = FALSE)
Lets bring that into Weka Explorer
Classify gives a much higher ROC etc
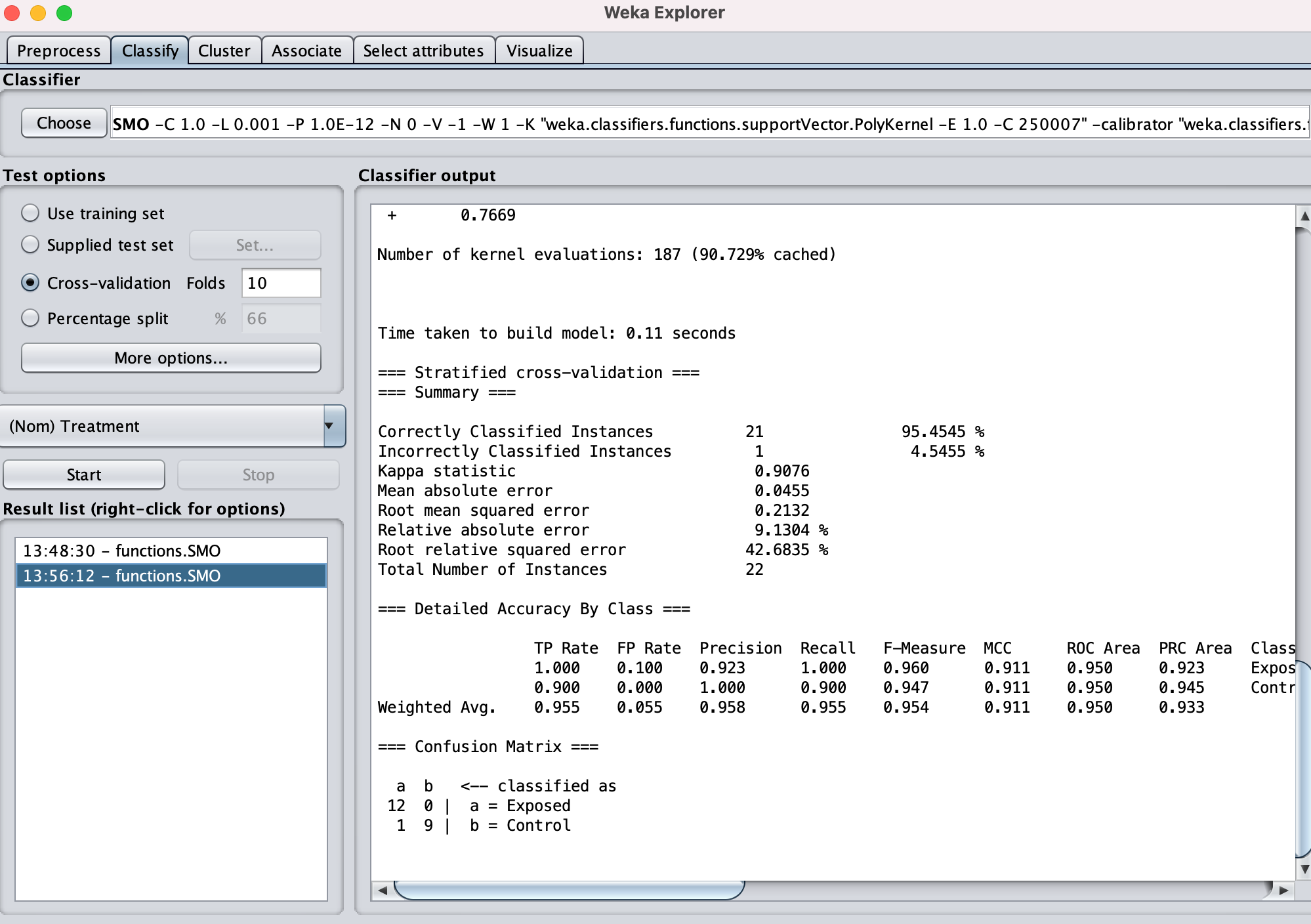
Summary
=== Stratified cross-validation ===
=== Summary ===
Correctly Classified Instances 21 95.4545 %
Incorrectly Classified Instances 1 4.5455 %
Kappa statistic 0.9076
Mean absolute error 0.0455
Root mean squared error 0.2132
Relative absolute error 9.1304 %
Root relative squared error 42.6835 %
Total Number of Instances 22
=== Detailed Accuracy By Class ===
TP Rate FP Rate Precision Recall F-Measure MCC ROC Area PRC Area Class
1.000 0.100 0.923 1.000 0.960 0.911 0.950 0.923 Exposed
0.900 0.000 1.000 0.900 0.947 0.911 0.950 0.945 Control
Weighted Avg. 0.955 0.055 0.958 0.955 0.954 0.911 0.950 0.933
=== Confusion Matrix ===
a b <-- classified as
12 0 | a = Exposed
1 9 | b = Control
This seems to suggest to me that these 24 gene expression patterns can confidently predict exposure, thus must be impacted by OA exposure, exclusive of sex.
But the next task is to identify what these genes are.
